Elc & Sac Providers
Aistear and Siolta Quality

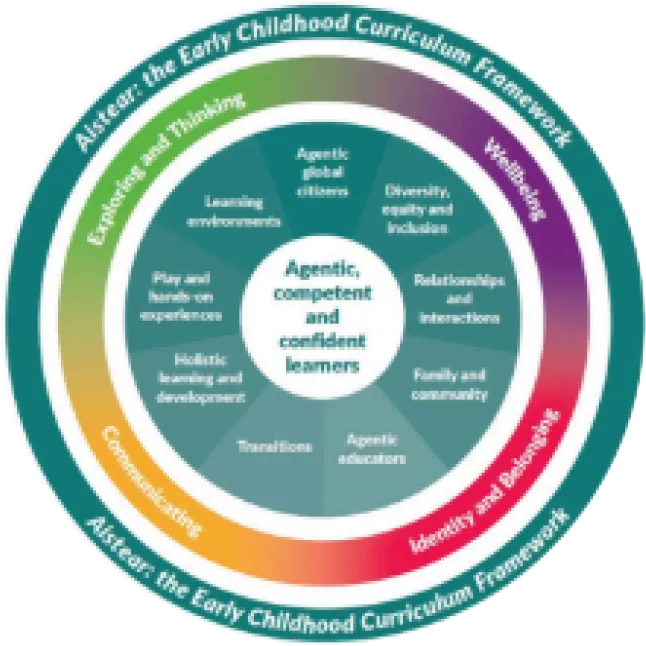
The Early Childhood Curriculum Framework was first published by the National
Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA) in 2009. Aistear was the first
curriculum framework for early childhood education in Ireland. It celebrates early
childhood as a time of being, a time for enjoying and learning from experiences as
they unfold, and laying important foundations for later learning and for life.
Because early childhood marks the beginning of babies, toddlers and young
children’s lifelong learning journeys, the Framework is called Aistear, the Irish
word for journey. An update of the Framework was undertaken to recognise and
reflect societal and policy changes that have taken place since the publication of
the original Framework. The update was also undertaken to reflect the pace of
educational research since the late 2000s and the new learning this gave rise to
about how babies, toddlers and young children learn and develop and how
educators can enrich and encourage this appropriately. It is envisaged that this
updated Framework will continue to support and enrich babies, toddlers and
young children’s learning and development. The updated Framework is supported
by the Guidance for Good Practice. The Guidance builds on the original
Guidelines for Good Practice (NCCA, 2009) and supports educators to
understand and engage with new concepts introduced in the updated
Framework. The use of digital technologies to support babies, toddlers and young
children’s learning will be promoted in line with Department of Children, Equality,
Disability, Integration and Youth, Department of Education and wider policy

Principles of Early Learning and Development Aistear is based on nine Principles of early learning and development. These are the foundation of the Framework and bring the curriculum vision to life. They are also embedded throughout the Framework’s Theme descriptors, Aims and Learning Goals.
Guidance for Good Practice.
Child Protection / Safeguarding
Safeguarding is a broad, proactive approach to prevent harm and create safe environments, while child protection is a reactive, more specific response to abuse and
neglect once a child is identified as being at risk or already harmed. Safeguarding involves organizational policies, staff training, and creating safe spaces, whereas
child protection involves specific actions like reporting, investigation, and intervention to address individual cases of harm.

Safeguarding
Child safeguarding in Ireland is a legal and multi-agency effort led by the Child and Family Agency (Tusla), which requires organizations to implement safety measures and mandates certain professionals to report concerns. The Children First Act 2015 is the key legislation, and key principles include the paramountcy of the child’s best interests and a responsibility for everyone to report concerns to Tusla if there are reasonable grounds to believe a child is at risk of abuse or neglect.
Children First
Children First National Guidance for the Protection and Welfare of Children 2017 was launched on October 2nd 2017. This Guidance is a primary reference for all citizens to report concerns and includes the new legislative obligations. It provides clarity between the legislation and the existing non-statutory obligations which will continue to operate for all sectors of society. Children First Guidance describes the four main types of abuse and sets out the steps which should be taken to ensure that the child or young person is protected from harm. It has been updated to include new information about the Children First Act 2015 and it includes specific information for the professionals and organisations that now have legal obligations to keep children safe
Protection
In Ireland, Tusla (the Child and Family Agency) is the primary body responsible for child protection. If you have concerns that a child is being, or is at risk of being, abused or neglected, you should report it to Tusla. You can also contact the Gardaí in an emergency or if you cannot reach Tusla, and schools and other organizations working with children have specific safeguarding procedures.
